what kind of chemicals are use to cleanse recycling waste water
Minimizing Wastewater from Cleaning Processes
Past John F. Russo
1 recent and prevalent trend has been an increment in the number and stringency of federal, state and local regulations concerning waste generated past reusing the cleaning chemicals and reducing and/or eliminating wastewater discharge.
The best wastewater treatment system should accept keen adaptability, depression environmental impact, low amount of hazardous waste, low ecology impact, low capital outlay and low operating costs.
The objective is to choose a chemic cleaner and equipment that cleans the parts while having the lowest operating cost for site-specific regulations such as air emissions, wastewater and solid waste material. The blazon and amount of cleaning chemicals used will touch on both wastewater (cleaning chemical and rinse wastewater) and solid waste product.
To select the optimum cleaning process, the corporeality of wastewater and solid waste generated should be considered every bit much as the cleaning equipment and cleaning chemistry themselves. No optimum cleaning process can be achieved with certainty unless cleaning chemical, cleaning equipment and wastewater treatment are considered simultaneously - the two major sources or wastewater contagion are the cleaning chemic and the rinse wastewater.
Some solvent and aqueous cleaning chemicals tin be reused numerous times. All the same, unless the chemic volume is reduced and hauled or discharged, disposal can be expensive. For aqueous cleaning chemicals, membrane filtration, such every bit microfiltration or ultrafiltration, can be implemented to reuse the chemical. Membrane filtration reduces wastewater generation past reusing the wastewater several times. Microfiltration membranes have a coarser rating of about 0.one to 1 micrometer accented, while ultrafiltration membranes are finer and rated at virtually i,000 to 1,000,000 molecular weight.
What to Choose
Choosing the all-time method of wastewater reduction depends on numerous factors, such as the key chemic ingredients' molecular weight and characteristics of the filtered contaminants. Testing on the bodily cleaning process is one of the better ways to determine the number of reuse cycles. Initial laboratory testing of the cleaning chemical - with or without the contamination - can give an initial indication of membrane compatibility and the feasibility of reuse. However, if the rest of the chemical ingredients are changed, the necessity of restoring the balance may be a limiting factor in its reuse.
The cleaning chemic sometimes requires treatment before belch, such as pH adjustment (most often the pH is also high), toxic metal removal or other conditions. However, sometimes a discharge is not possible or undesirable, making hauling necessary.
Evaporative processes can also prove to be price-constructive. Since the rinse water contains an extremely low level of cleaning chemicals, it will typically run across the local discharge regulations without treatment. Still, in some applications information technology is desirable to reduce and even eliminate rinse h2o discharge. The possible reasons may include cost effectiveness of recovering high purity rinse water, restrictions of water usage or a local ordinance preventing all discharge. In that location are two general methods used to accomplish this purpose. The ability to recycle wastewater rinses depends continuously on the characteristics of the contaminants. For aqueous, and, to a much lesser extent solvent cleaning, deionization is the central procedure. The ion-exchange resin continuously removes the process contamination and tap water, if tap water is used equally makeup water to recoup for process water losses. If the contaminants are not removed continuously, they accumulate in the system and mayhap redeposit on the parts being cleaned.
One or more of the following complementary processes such as mechanical filtration, activated carbon and membrane (reverse osmosis, ultrafiltration or microfiltration) are needed. Depending on the process requirement, mechanical filtration removes particles i micrometer and higher up. Activated carbon removes low levels of organic compounds (solvents, surfactants and others). Membranes tin can remove a big multifariousness of particles such every bit dissolved minerals down to the ionic range. For contrary osmosis membranes, the wastewater is converted to water with purity ranging from 25,000 ohm-cm to 800,000 ohm-cm. If college water purity is required, deionization can polish the wastewater upwardly to 16.0 megohm-cm and college. Ultrafiltration membranes are skilful for separating organic molecules from a wastewater stream. Typically, it is used to remove low molecular weight organic molecules (depending on the membrane molecular weight rating) such as oils or breaking oily emulsions. Microfiltration is primarily used to remove fine particles and breaking oily emulsions, but it can non remove the depression molecular weight organic molecules that the ultrrafilter tin. Also, neither ultrafilter nor microfilter membranes remove ionic species that the reverse osmosis membrane removes. Even though both membrane and microfiltration membranes are used to recycle cleaning chemicals, they can pretreat a wastewater (oily type) used in a closed-loop process prior to other purification methods such as reverse osmosis membrane or ion-exchange resin. The reject stream from any of these membranes is either reduced in volume by evaporation or hauled to a treatment facility.
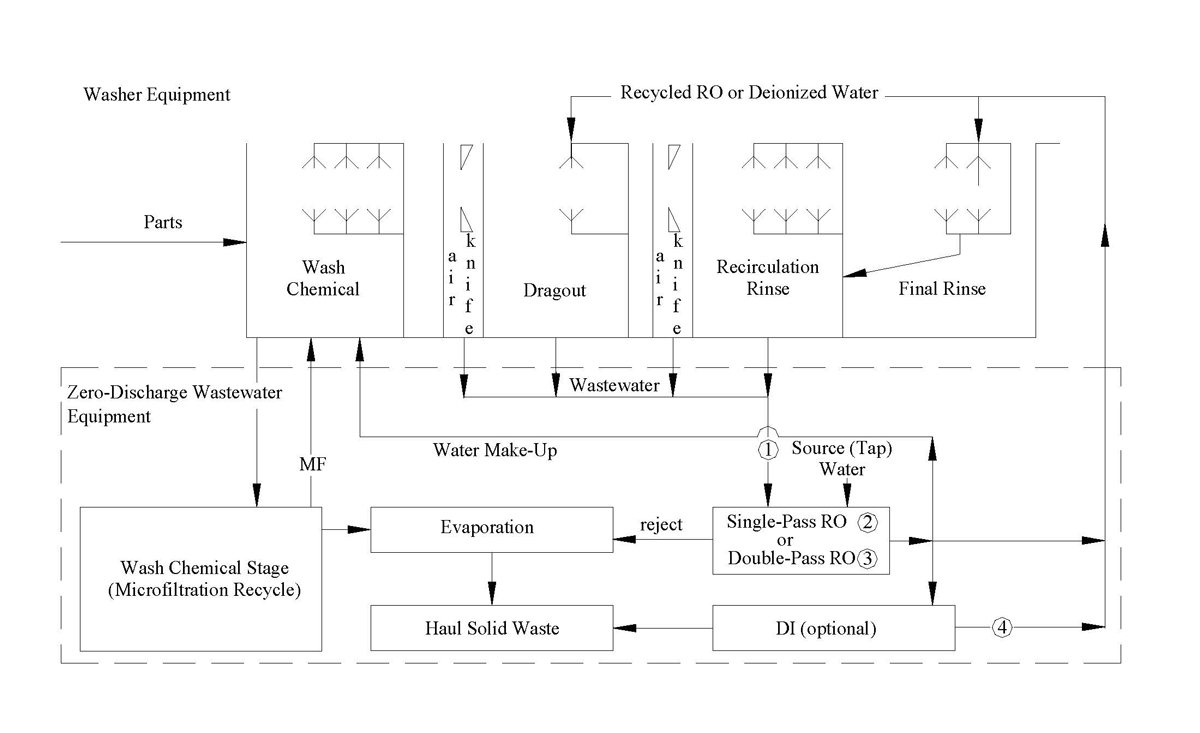
(Click Image to View Larger Version)
This schematic shows an alkaline wastewater handling system using iii separation technologies: evaporative, membrane (opposite osmosis) and ion exchange. The concluding rinse water component uses a closed-loop ion-exchange arrangement. The membrane issued information technology separate the high ionic contamination from the dragout section into two streams, a reusable low purity water as makeup to the closed-loop system and a reusable alkaline cleaning chemical stream. Without the contrary osmosis membrane treating the wastewater from the dragout section of the cleaning equipment, the very high ionic content of the wastewater makes the final rinse water-recycling unit, which uses ion-exchange resin too expensive to operate. The evaporator further reduces the corporeality of spent cleaning chemical and the overflow from the wash tank caused by the excessive reject from the membrane. Other system designs tin can apply one or more of the separation technologies depending on the awarding. For low book batch operations an evaporator or only a closed-loop component may be used. If the discharge regulations are not a business organization, then the membrane alone can be used to recycle the high water purity water while the turn down stream tin exist discharged to the bleed, if it meets the regulations.
One time y'all have minimized the corporeality of wastewater generated by the cleaning process, the solid waste disposal needs to be considered. Alkaline cleaning baths or spent solvents are solid wastes, even though they are actually liquids and sludges, per the federal EPA definition. As already mentioned, dewatering processes such as evaporation can be very effective in reducing disposal costs peculiarly for chancy wastes. Disposal costs may exist equally high as $5000.00 per 55-gallon pulsate. Other solid wastes, such as filters will accept to exist disposed of as they are or even incinerated depending on the contamination that may cause a regulated emission. Reducing the amount of this not-liquid and sludge solid waste depends on the option of filters. The best selections are those filters with the highest removal of contaminants at the everyman cost. For the ion-exchange resins, reuse is possible depending on numerous factors such as the water purity desired, type of contaminants beingness removed and shipping costs.
The selection of separation technologies and system designs tin be an important strategy in avoiding the nomenclature of some solid wastes as hazardous. The Federal EPA standard for classification of solid wastes, the "TCLP" test, is used with few exceptions past most states to classify wastes equally hazardous. It is possible to avoid the chancy waste nomenclature by knowing the test criteria and the peculiarities of the test method.
Summary
The minimization of the amount of wastewater generated by a cleaning process depends on numerous factors. By simultaneously evaluating the entire cleaning process by cleaning chemical science, cleaning equipment and wastewater treatment equipment, you will accomplish your objective with minimal uppercase and operating costs.
Compatibility of Temporary H2o Soluble Spot Mask and Defoamer Soldering Chemistries in a Closed-Loop Water Recycling System
Temporary Water Soluble Mask
Case History - A closed-loop wastewater recycling user was dissatisfied with the spot mask that he was using because it was leaving a residue inside the cleaner. The accumulated balance inside the windows left doubts nearly the cleanliness of the printed excursion boards.
Solution - Afterwards testing several types of mask he found one that performed best for his application. The employ of this mask produced an immediate positive consequence - there was no residuum accumulation! Equally he continued to use the mask other benefits became apparent such equally reduced pump repairs, frequency of cleaning the cleaner and, most chiefly, the achievement of a substantially longer media life. After comparing the operating costs, he establish that they were reduced from $10,000 per yr to $vii,000 per year. Since this experience, SepTech has used this specific mask and has found that it will always reduce the operating costs of the recycle organization in comparing to other brands of spot masks.
Defoamer
Case History - A new AquaCycler was started-up and the water purity varied from 10 to 18 megohm-cm for a few days. On i occasion the water purity suddenly dropped to 450,000 ohm-cm simply the water regained its higher purity level over the next few days. Notwithstanding, on another occasion, later adding the defoamer, the engineer noticed that the improver of 2 capfuls of defoamer caused the water purity dropped from most 10 megohm-cm downwardly to 150,000 ohm-cm in minutes! This amount of defoamer was necessary to reduce the foam level earlier it overflowed from the cleaner wash tank.
Solution - The water recycling system could now operate without existence prohibitively expensive. In addition, there was no visible decrease in the water purity and only 5 drops were needed to accomplish the aforementioned issue every bit 2 capfuls of the other brand!
Source: https://www.separationtech.com/technical_papers.php
0 Response to "what kind of chemicals are use to cleanse recycling waste water"
Post a Comment